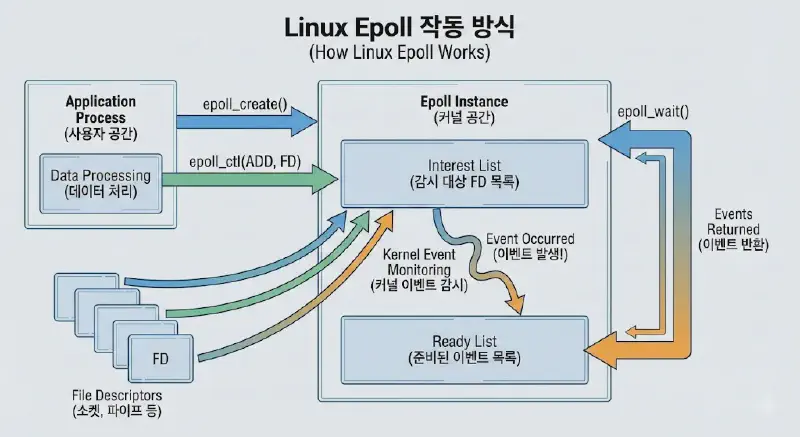
Epoll? #
Epoll is an I/O notification model designed in Linux to supplement the disadvantages of select.
File descriptors (FDs) are managed by the kernel rather than the user, which means the CPU does not need to constantly monitor the status changes of file descriptors.
In other words, while select requires a loop (using FD_ISSET) to sequentially search through all file descriptors to find which one triggered an event, Epoll passes only the file descriptors where events have actually occurred via a structure array. This significantly reduces the cost of memory copying.
Epoll Functions #
epoll_create #
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_create(int size)You need to create a space to store I/O events for FDs. epoll_create creates a space to store as many I/O events as specified by size.
However, since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is ignored, but it must still be set to a value greater than 0. The kernel dynamically adjusts the size of the necessary data structures, so providing any positive integer suffices.
The return value is an integer, commonly referred to as the epoll fd. This fd is used to manipulate the FDs registered in epoll.
epoll_ctl #
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event)epoll_ctl is a function used to register, modify, or delete FDs in epoll. It is generally described as an interface to register an FD you want epoll to monitor and the type of event you are interested in for that FD.
- epfd: The epoll fd value.
- op: An option value indicating whether to add a new FD, change the settings of an existing FD, or remove an FD from the monitoring list.
EPOLL_CTL_ADD: Adds the FD to theepfdinterest list. If it already exists, anEEXISTerror is generated. The event set is stored inevent.EPOLL_CTL_MOD: Changes the settings of an FD using the information specified inevent. If the FD is not in the interest list, anENOENTerror is generated.EPOLL_CTL_DEL: Removes the FD fromepfd. If the FD is not in the interest list, anENOENTerror is generated. If an FD is closed, it is automatically removed from the epoll interest list.
- fd: The value of the file descriptor to be registered in
epfd. - event: A structure specifying which events to monitor for the registered FD. It defines the observation type of the target.
typedef union epoll_data
{
void *ptr;
int fd;
__uint32_t u32;
__uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t
struct epoll_event
{
__uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
}| Events | Description |
|---|---|
| EPOLLIN | Data is available to be read. |
| EPOLLOUT | Writing is possible. |
| EPOLLPRI | Urgent data (OOB) is available. |
| EPOLLRDHUP | Connection closed or Half-close occurred. |
| EPOLLERR | Error occurred. |
| EPOLLET | Set to Edge Trigger behavior (Default is Level Trigger). |
| EPOLLONESHOT | Receive the event only once. |
epoll_wait #
#include <sys/epoll.h>
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event * events, int maxevents, int timeout)epoll_wait investigates what happened to the FDs of interest. However, the result is different from select or poll.
It returns a list of events via the (epoll_event).events[] array. The return value is the number of events that occurred.
- events: A structure array that gathers FDs where events occurred.
- maxevents: Specifies the maximum number of events to process at once, regardless of the actual number of concurrent connections. If there are 10,000 connections, events could effectively occur on all 10,000 in a worst-case scenario. While you would need to allocate memory for an
events[]array of 10,000, thismaxeventsparameter allows you to limit the number of events you wish to process in a single call. - timeout: An important element specifying the behavior of
epoll_wait, defined in milliseconds. It means “wait for an event for this amount of time.” If an event occurs while waiting, it returns immediately.- If
timeoutis -1, it enters a blocking state, waiting forever for an event. - If
timeoutis 0, it checks for events and returns immediately, regardless of whether events exist.
- If
Example Scenarios:
Consider a simple chat server. The server needs to work only when a user sends data. If no one says anything, the server has no reason to process. In this case, set
timeoutto -1 to yield processing time to the OS while there is no user input.In the case of online games (especially MMORPGs), even if there is absolutely no user input, the server must process monster logic, appropriate saves, and communication with other servers. Therefore, an appropriate
timeout(I prefer 1/100 sec, i.e., 10ms) should be specified.If you want to handle communication events intermittently while mainly performing some processing (i.e., you want to occupy high CPU usage to do something), you can design it to monopolize the CPU by setting
timeoutto 0.If you are writing a program with a separate thread dedicated to I/O, naturally, you should set
timeoutto -1 to return the remaining time to other threads or the operating system.
Edge Trigger & Level Trigger #
Edge Trigger (ET) #
Detects only at the moment a specific status changes.
If a specific digital signal is 000 111 000 111 000 111, an event occurs only at the moment the signal changes from 0 to 1.
Mapping this to a socket buffer: If the readable data buffer size is 600 bytes, but 1000 bytes of data arrive, and you read only 600 bytes, no further events will occur even though 400 bytes remain unread.
This is because, based on the point of reading, there is no further change in status.
Therefore, if data larger than the readable byte size arrives at once, additional work must be done separately.
To operate in ET mode, the socket must be created as Non-blocking, and EPOLLET must be set when registering the interest FD in epoll.
If the server’s trigger mode is Edge Trigger, and the size of the data to be sent is larger than the packet buffer size capable of being sent at once, causing the write to happen multiple times, there may be cases where data cannot be fully read normally due to the nature of Edge Trigger.
Level Trigger (LT) #
Detects as long as a specific status is maintained.
In the digital signal example 000 111 000 111 000 111, if the trigger is for ‘1’, events occur regardless of the count as long as ‘1’ is maintained.
Mapping this to a socket buffer: If the readable data buffer size is 600 bytes, but 1000 bytes of data arrive, you read 600 bytes. Since the socket buffer still has data (status is ‘1’), another event occurs, causing the remaining 400 bytes to be read. In other words, events continue to occur until the socket buffer becomes empty (becomes 0).
LT is the default setting, and select or poll supports only LT.
If the server’s trigger mode is Level Trigger, and you do not quickly read the data when it is received in the input buffer, an event will occur every time epoll_wait() is called. This causes the number of events to accumulate continuously, which is practically impossible to handle. Consequently, normal connection/disconnection testing processes may become impossible.
Code #
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
using namespace std;
#include <sys/unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
/**
* In a general connection setup, the client sends a connection request using connect(), and the server accepts it using accept().
* However, if the server is busy with other tasks, it may not be able to accept(). In this case, the connection request waits in a queue.
* 'backlog' is the maximum number of connection requests that can wait without being accepted.
* Usually, a value of around 5 is used. If a very large value is used, it consumes kernel resources.
* Therefore, it represents the maximum number of clients waiting for a connection, not the maximum number of connectable clients.
*/
#define LISTEN_BACKLOG 15
int main()
{
printf("hello from Leviathan_for_Linux!\n");
int error_check; // Socket creation
int server_fd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (server_fd < 0)
{
printf("socket() error\n");
return 0;
}
// Set server fd to Non-Blocking Socket. Configured to use Edge Trigger.
int flags = fcntl(server_fd, F_GETFL);
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
if (fcntl(server_fd, F_SETFL, flags) < 0)
{
printf("server_fd fcntl() error\n");
return 0;
}
// Set socket options.
// Option -> SO_REUSEADDR : Allow port reuse on abnormal termination
int option = true;
error_check = setsockopt(server_fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &option, sizeof(option));
if (error_check < 0)
{
printf("setsockopt() error[%d]\n", error_check);
close(server_fd);
return 0;
}
// Set socket attributes
struct sockaddr_in mSockAddr;
memset(&mSockAddr, 0, sizeof(mSockAddr));
mSockAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
mSockAddr.sin_port = htons(1818);
mSockAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // INADDR_ANY : Use available LAN card IP
// Bind socket attributes to socket fd
error_check = bind(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&mSockAddr, sizeof(mSockAddr));
if (error_check < 0)
{
printf("bind() error[%d]\n", error_check);
close(server_fd);
return 0;
}
// Wait for connection
if (listen(server_fd, LISTEN_BACKLOG) < 0)
{
printf("listen() error\n");
close(server_fd);
return 0;
}
// Create Epoll fd
int epoll_fd = epoll_create(1024); // Function to create kernel polling space of size
if (epoll_fd < 0)
{
printf("epoll_create() error\n");
close(server_fd);
return 0;
}
// Register server fd to epoll
// EPOLLET => Use Edge Trigger
// If we correspond Level Trigger and Edge Trigger to a socket buffer:
// Level Trigger judges based on the level of the socket buffer, i.e., the presence of data.
// Even if you read and processed it, if you didn't read fully, the event continues to occur.
// For example, if 1000 bytes arrived and you read only 600 bytes, Level Trigger continues to generate events.
// However, in Edge Trigger, even if you only read 600 bytes, no further events occur.
// This is because there is no further state change based on the moment of reading.
// LT or ET can easily be set as an option.
// Note that select / poll supports only Level Trigger.
struct epoll_event events;
events.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
events.data.fd = server_fd;
/* server events set(read for accept) */
// epoll_ctl : Interface to register the FD epoll should monitor and the event occurring on that FD.
// EPOLL_CTL_ADD : Add interesting file descriptor
// EPOLL_CTL_MOD : Modify existing file descriptor
// EPOLL_CTL_DEL : Delete existing file descriptor from interest list
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, server_fd, &events) < 0)
{
printf("epoll_ctl() error\n");
close(server_fd);
close(epoll_fd);
return 0;
}
// epoll wait.
// Investigate what happened to FDs of interest.
// The list of events is passed to the epoll_events[] array.
// Return value is the number of events, max number of events is MAX_EVENTS
// timeout -1 --> Wait for event forever (blocking)
// 0 --> Do not wait for event.
// 0 < n --> Wait for (n)ms
int MAX_EVENTS = 1024;
struct epoll_event epoll_events[MAX_EVENTS];
int event_count;
int timeout = -1;
while (true)
{
event_count = epoll_wait(epoll_fd, epoll_events, MAX_EVENTS, timeout);
printf("event count[%d]\n", event_count);
if (event_count < 0)
{
printf("epoll_wait() error [%d]\n", event_count);
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < event_count; i++)
{
// Accept
if (epoll_events[i].data.fd == server_fd)
{
int client_fd;
int client_len;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
printf("User Accept\n");
client_len = sizeof(client_addr);
client_fd = accept(server_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, (socklen_t*)&client_len);
// Set client fd to Non-Blocking Socket. Configured to use Edge Trigger.
int flags = fcntl(client_fd, F_GETFL);
flags |= O_NONBLOCK;
if (fcntl(client_fd, F_SETFL, flags) < 0)
{
printf("client_fd[%d] fcntl() error\n", client_fd);
return 0;
}
if (client_fd < 0)
{
printf("accept() error [%d]\n", client_fd);
continue;
}
// Register client fd to epoll
struct epoll_event events;
events.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
events.data.fd = client_fd;
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, client_fd, &events) < 0)
{
printf("client epoll_ctl() error\n");
close(client_fd);
continue;
}
}
else
{
// Handle send data from clients registered in epoll
int str_len;
int client_fd = epoll_events[i].data.fd;
char data[4096];
str_len = read(client_fd, &data, sizeof(data));
if (str_len == 0)
{
// Client disconnect request
printf("Client Disconnect [%d]\n", client_fd);
close(client_fd);
epoll_ctl(epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, client_fd, NULL);
}
else
{
// If not a disconnect request, process according to content.
printf("Recv Data from [%d]\n", client_fd);
}
}
}
}
}

